This web page was produced as an assignment for Gen677 at UW-Madison Spring 2009
Steroids in Plant Development
Introduction
Hormonal communication is an integral part of mammalian development and disease. However, not so much is known role these compounds play in other organisms. A number of steroids have been identified in plant species, most notably the Brassinosteroids. With the advances in genomic sequencing, it has also been shown that the enzymes responsible for the biosynthesis of these molecules in plants are homologous to the 5 alpha reductases in humans (SRD5A2 for example).
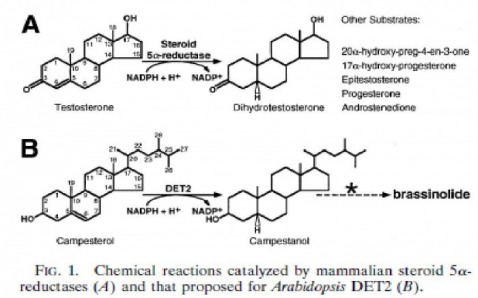
Figure one above from Li's paper shows the similar reactions of both enzymes. This homology in such an unrelated set of organisms may shed some light on the evolutionary history of steroidal communication and its role in development (1).
Sequence Homology
T-Coffee analysis reveals the similarities and differences of the homologous structures of a steroid biosynthesis enzyme found in humans (SRD5A2) and in Arabidopsis (DET2). Most important are the highly conserved regions near the N-Terminus and near the center of the sequence. These regions of similarity correspond to the enzymes respective active sites and impart the similar biochemical functioning in the representative organisms (1).
Bald Plants
Well not quite, but the effects of a mutagenized SRD5A2 homolog is pretty significant. Mutations in the DET2 gene result in uncoupling downstream light dependent processes which are dependent on the Brassinosteroids. This results in dark-grown plants being more similar to light grown plants (see pictures below). They exhibit hypocotyl growth inhibition, cotyledon expansion, primary leaf initiation, anthocyanin accumulation, and derepression of light-regulated gene expression (2).
Pictures from The Arabidopsis Information Resource (TAIR)
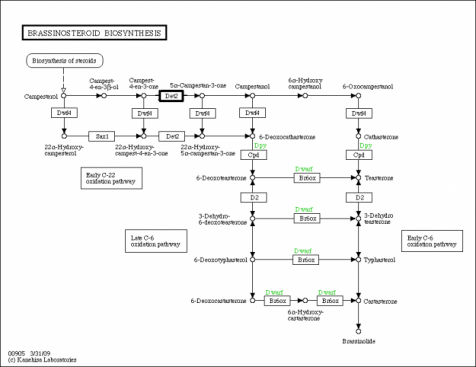
Biosynthesis of Brassinosteroids
You can see that DET-2 occurs early in the sequence of reactions, which explains why mutations here can have such detrimental effects.
Protein Interactions
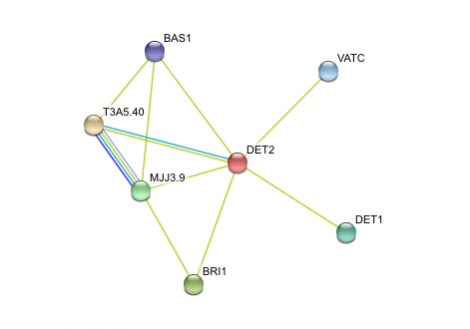
The STRING interaction web shows the DET2 is involved with multiple other proteins. One of the most omprtant is DET1, which is involved in leight mediated development as well. VATC is an ATP synthase subunit C protein. Since DET2 is involved in light mediated reactions, which would most likely involved energy expediture, a close interaction with the energy production in the cell would be necessary. T3A5 is similar to the Aromatase protein in the human network and is a steroid hydroxylase. It probably involves the conversion of Brassinosteroids to a different signalling pathway or degradation.
References
1. Li, J., Biswas, M.G., Chao, A., Russell, D.W., and Chory, J. (1997) Conservation of function between mammalian and plant steroid 5 alpha reductases. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 94:3554-3559
2. Chory, J., Nagpal, P., and Peto, C.A. 1991. Phenotypic and Genetic Analysis of det-2, a new mutation that affects light regulated seedling development in Arabidopsis. The Plant Cell. 3(5):445